– Potential of Dutch deep tech industry
– What deep tech technology is the Netherlands looking for?
European deep tech industry
Although 'Deep Technology' is difficult to define in one word as much as the level of technology being dealt with, it usually refers to technology based on cutting-edge science or engineering. Most deep tech requires a long research period, large investment, and takes a relatively long time to commercialize. It covers a wide variety of high-tech fields such as AI, machine learning, big data, language processing, vision and speech algorithms, robotics, blockchain, advanced materials science, optoelectronics, biotechnology, and quantum computing.
The European Union (EU) is investing heavily in these deep-tech industries, and the combined value of deep-tech companies established in Europe is about 2020 billion euros as of 7,000, continuing a very steep growth. Among them, the value of companies established before 2000 is 5,080 billion euros, leading the industry, and the value of companies established after 2000 is estimated at 1,880 billion euros.
<Deep tech companies to pay attention to>

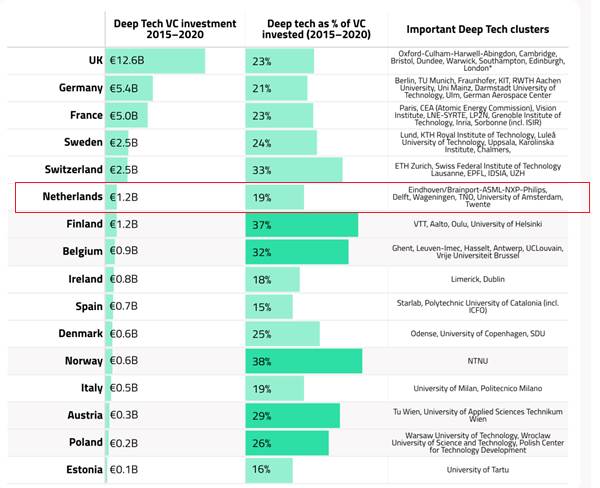
European deep tech companies are based on higher education institutions and receive initial capital support through government subsidies. In order to rapidly raise the level and potential of the deep tech industry, it is necessary to closely coordinate policies that can support promising and capable deep tech startups. European deep tech investment in 2015-2020 was led by VCs from the UK, Germany and France, while the Netherlands took 12th place with a total investment of 6 billion euros in the deep tech sector. Looking at the ratio to the total investment amount during the same period, VCs from Norway, Finland, and Belgium invested 30% or more of their investment in the deep tech sector, showing the highest ratio, while the Netherlands recorded 19%.
<European deep tech industry investment status>
Dutch deep tech industry
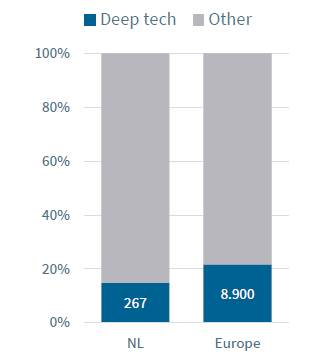
The Netherlands, which attracted an investment of 2020 billion euros in the tech startup industry in 18, sees the startup industry as a driving force for national growth and is supporting it. Despite the high risk and long R&D period due to the nature of the industry, it is attracting a lot of attention for its attractiveness, innovativeness, and potential. However, in the Netherlands in 2020, only 2% of a total of 6,700 million euros was invested in the deep tech industry, which was slightly lower than the European average of about 15%.
<Comparison of investment status in deep tech sector in 2020>
(Unit: million euros)
The Dutch government is reviewing government support strategies to consider how to effectively use limited resources, although financial support is important for the growth and expansion of the deep tech startup industry. In this regard, Techleap commissioned an organization consulting agency Birch to investigate the potential of the Dutch deep-tech industry in June 2021. Techleap is a public interest non-profit organization aimed at developing the Dutch startup industry.
Dutch deep tech potential
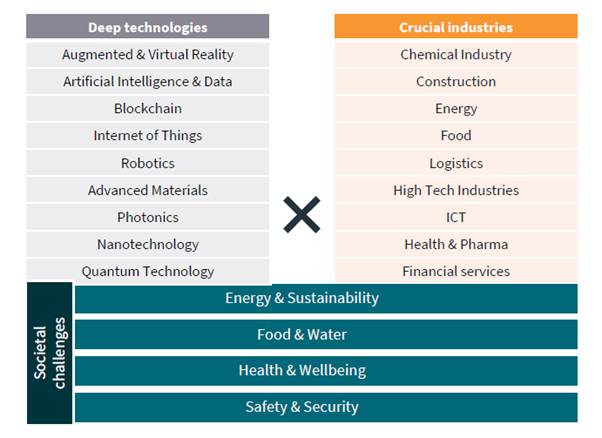
According to Birch's research, industries that can utilize deep tech technology in the Netherlands can be classified into nine categories: chemistry, architecture, energy, food, logistics, high-tech, ICT, pharmaceutical and medical care, and finance. expected to be applicable to The advanced technology developed through such deep-tech research is expected to become the core of a promising technological innovation field for the next 9 years. He also mentioned that by promoting the growth of the deep tech industry, the national economy and international competitiveness can be strengthened through job creation and technology export.
<Industries expected to apply deep tech technology>
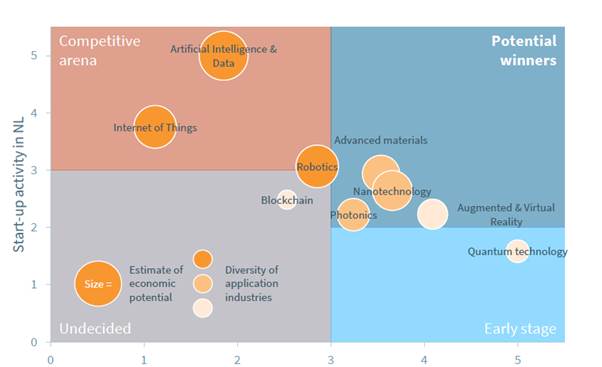
The research institute analyzed the activities of Dutch deep-tech startups by dividing them into areas with current competitiveness, fields with great potential, fields in the early stages, and areas where competitiveness is difficult to judge yet. First, the fields of artificial intelligence (AI), data, Internet of Things (IOT), and robotics were selected as the fields with the greatest competitiveness with various industrial application cases. New materials, nanotechnology, and photonics technology belong to fields with great potential, and augmented and virtual reality, quantum technology, and block chain technology, although there are some differences, are classified as fields that are not yet relatively competitive.
<The Dutch Promising Deep Tech Field>
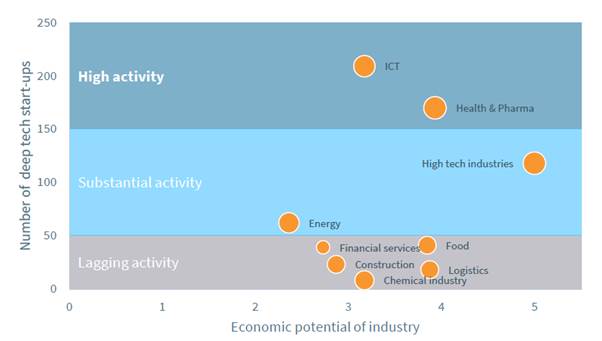
On the other hand, when evaluating the number and economic potential of start-ups in the Netherlands, ICT and healthcare were clearly selected as promising fields in the deep tech industry. In the Netherlands, the purpose of this industry is to strengthen its international competitiveness by discovering the right application fields and expanding its scale. Excluding ICT and healthcare, business activities in high-tech and energy industries are active, focusing on expanding the market size and lowering barriers to entry for more companies to participate. Lastly, the food, construction, logistics, chemical, and financial services sectors were found to have little business activity in deep tech yet. In the long term, the Netherlands will set a support direction so that deep tech can lead industrial improvement through innovative technology development even in these unpopular industries.
<Deep Tech Startup Activity Distribution Chart>
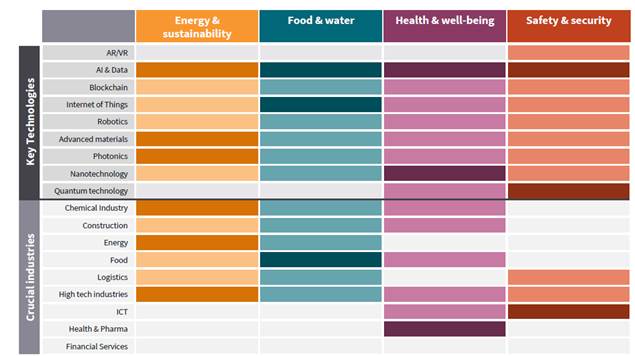
Furthermore, the data below shows links to the Dutch innovation policy tasks that can be improved by applying deep tech. Artificial intelligence, data, Internet of Things, photonics, nanotechnology, and quantum technology are solving one or more policy tasks, and the policy tasks are broadly divided into four categories: energy and sustainability, food, health, safety and security.
<Skills necessary to solve social problems>
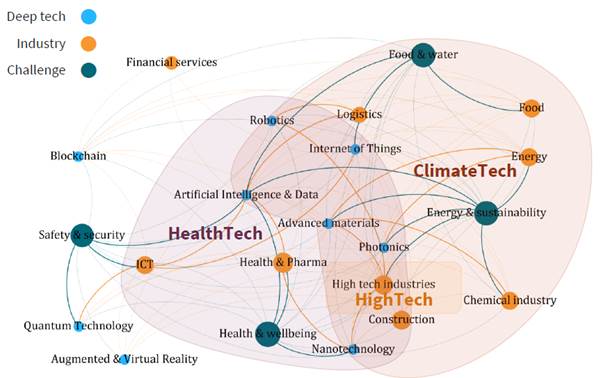
Another characteristic of the deep tech field is that the boundaries between industries are not clear and various connections can be made. do. It is expected that this kind of inter-industry exchange will create very great value for the Dutch innovative industry.
<Link between deep tech technology and industry>
The Netherlands ranks in the top 4 in the world for the four major deep-tech research achievements, accounting for only 10% of the world's population, but accounting for 0.2% of research output. Among the 2.1% most cited international papers, Dutch scholars account for 1%. The Netherlands is particularly leading the field in advanced materials, robotics, augmented and virtual reality.
In addition, although the Netherlands is not a top country in terms of photonics technology and nanotechnology production, it ranks in the top 10 in terms of production quality (FWCI), which has a collaboration rate between companies that is more than three times the global average. In this field, Philips Healthcare and ASML are considered industry leaders. In the field of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, the Dutch industry is small compared to the leading countries, but the production quality is about 3 times the world average.
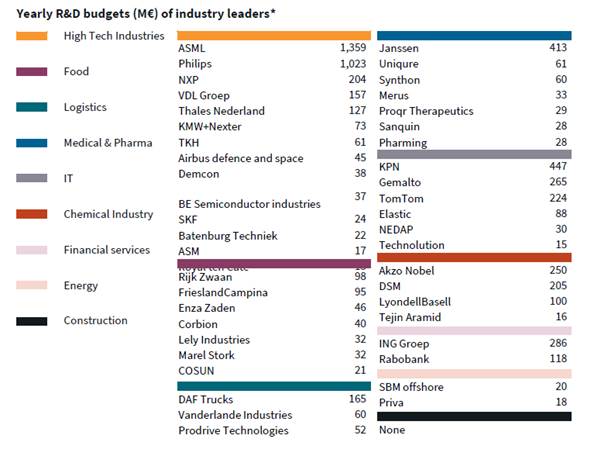
Among the leading companies in the world's high-tech industry, you can find many Dutch companies, which develop technologies through large-scale R&D and bring these advanced technologies to the market. They partner with other research institutions to form spin-offs and make generous investments. ASML and Philips invest more than €10 billion annually in R&D, while Janssen and KPN allocate €4 million and €1,300 million respectively for R&D. In particular, the high-tech, food, ICT, and chemical industries are actively investing in R&D in proportion to their large scale, which has high economic potential in the future. In addition, many companies are developing technologies in various deep tech clusters such as Eindhoven, Delft, Wageningen, Amsterdam, and Gwente in the Netherlands.
<Annual R&D budget for leading Dutch companies and companies>
(Unit: million euros)
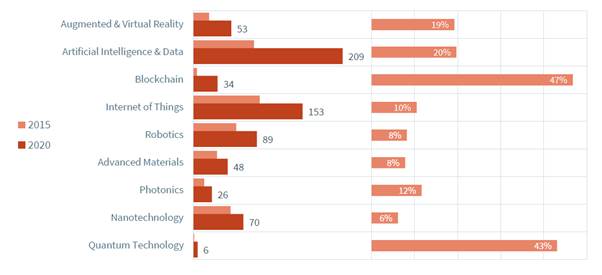
Within the deep tech industry, start-ups with software technology are growing faster. Startups in the deep tech industry, which require large-scale hardware investments, such as nanotechnology, advanced materials, robotics, and photonics, showed a lower growth rate than software (AI)-related startups. The number of hardware-based startups grew at a CAGR of 2015% from 2020 to 8, while software-based startups grew by 15%.
<(Left) Number of startups by field and (Right) Annual average growth rate (2015-2020)>
Industry Outlook
Many of Europe's top deep tech companies started out in schools and laid the groundwork for early growth through government subsidies. Marc Hendrikse, president of the Dutch High-Tech Association, noted that the startup industry has developed rapidly in recent years, and the support of Tech Leap, a public non-profit organization, has been of great help. Nevertheless, he said that many startups are still struggling to grow due to financial problems. The Dutch government, aware of these difficulties, has also created a 'deep tech fund' to support startups in the deep tech sector. Chairman Mark Hendrixe said it will take some time for the market to see an effect, but the budget that can be supported through Invest NL is 3 million euros per year, and there are funds and pension funds to support the deep tech industry. It is expected that more vitality will be added.
Currently, in the Netherlands, technology industries related to climate, chemical, construction, logistics, and biotechnology are considered as industries with great economic potential and social impact, but with few market participants. Interest and expectations for deep tech are growing not only in the Netherlands but also around the world, but the technology in all fields is not yet available in the market. Your chances of success will be greater.
Supported by: Betul Bulut, Amsterdam Trade Center
Sources: techleap.nl, techcrunch.com, deeptechequitynl.com, birch.nl, sifted.eu, eic.ec.europa.eu, dealroom.co, medium.com, innovationorigins.com



