– Completed installation of 26'Smart Poles' equipped with customized functions for each location, such as the Seoul Plaza and the Cheonggyecheon area
– Expansion of installation area to Guro and Dongjak-gu this year… 80 billion won in project cost by selecting MOLIT project
– At the end of this year, a pilot project for upgrading smart pole functions, such as charging drones and electric vehicles, and monitoring parking and stopping, will be promoted.
– 10 standard models of smart poles, construction and operation guidelines are also prepared... Applied to replacement/newly installed streetlights and traffic lights
□ The Seoul Metropolitan Government has built 6'smart poles' in 26 locations, including Seoul Plaza, Sungnyemun, and Cheonggyecheon. It is the core infrastructure of a smart city that integrates road facilities such as streetlights and traffic lights that are complexly installed all over the road, and combines ICT technologies such as public Wi-Fi and intelligent CCTV.
○'Seoul City Smart Pole (S-Pole)' not only performs its own function of road facilities (traffic lights, street lights, CCTV, security lights, etc.), but also smart devices such as public WiFi, intelligent CCTV, Internet of Things (IoT), and smart crosswalks. It is a model that has evolved into a smart holding infrastructure by fusion application of urban technology. It plays a role in improving urban aesthetics and enhancing civic safety, welfare, and convenience.
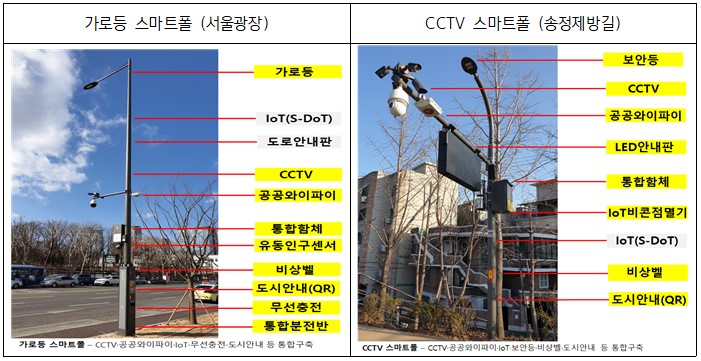
□ Each smart pole is equipped with a customized function that reflects the characteristics of each place in addition to the basic function as a road facility. For example, a free public Wi-Fi'Kachion' was installed in Seoul Plaza, where many citizens gather, a QR code to view cultural property information in Sungnyemun, and a video emergency bell for safety on the Songjeongjebang-gil along the Jungnangcheon stream, a trail that residents enjoy. .
○ Seoul Plaza: Traffic lights, street lights, public WiFi, intelligent CCTV, S-DoT S-DoT (Smart Seoul Data of Things) is an IoT city data sensor installed to establish a data-based smart city policy by checking various urban phenomena. , Fine dust, ultra-fine dust, noise, illuminance, temperature, humidity, ultraviolet rays, vibration, wind direction, wind speed, number of visitors, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, ozone, black bulb temperature 17 types of data collected by self-manufacture complex It is a sensor
(17 types of IoT sensors), a traffic light smart pole, and a street light smart pole combined with a smart phone wireless charging function were installed. As it is a place where many citizens gather, it provides a public Wi-Fi 6 Cation service so that high-quality data can be used free of charge throughout the plaza.
○ Sungnyemun: A streetlight smart pole that combines information such as Sungnyemun introduction, photos, and directions for city guide QR code, free public WiFi, intelligent CCTV, and S-DoT was installed.
○ All areas of Cheonggye 1-ga road along the Cheonggyecheon stream: A streetlight smart pole that combines streetlights, CCTV, S-DoT, and floating population measurement sensors is installed to check urban phenomena and provide civil safety services.
○ Songjeongjebang-gil along Jungnangcheon Stream: A smart pole that combines CCTV and security has been installed. Public WiFi, S-DoT, video emergency bell, IoT beacon linked to women's safety, and wireless charging functions for smartphones were also applied.
○ Roadside of Seongdong-gu Office: Traffic lights, street lights, and CCTV posts that were individually installed were combined into one, and a smart pole, a traffic light that combined public Wi-Fi, S-DoT, and smart crosswalk functions, was installed.
○ Seongdong-gu Youth Street Area: Ssamji Park Smart Pole near Wangsimni Station, where a lot of young people gather, is equipped with a signage display and energy-saving wind power generation function. It allows citizens to use it for events such as birthday celebrations and proposals, and usually provides a city guide function.
□ These 26 smart poles were completed for the first time by the Seoul Metropolitan Government. Based on these cases, the city has prepared 10'smart pole standard models' and construction and operation guidelines to be applied to smart poles in the future. It can be customized according to various urban environments and road conditions.
□ The city will expand the installation area to Guro-gu and Dongjak-gu this year, and at the end of the year, promote a pilot project to enhance the functions of smart poles.
□ Guro-gu and Dongjak-gu were recognized for the effectiveness and excellence of the Seoul Smart Pole pilot project, and were selected as target sites for the “2021 Smart City Solution Expansion Project” by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport. Each project cost 40 billion won. It is significant in that it accelerated the establishment of smart poles and laid a foothold for spreading across the country.
○ Seoul City was selected as the target site for “Smart City Solution Expansion Project in 2021” by jointly applying with Guro-gu and Dongjak-gu.
○ A streetlight smart pole that combines CCTV, public WiFi, and IoT technology LoRa (Long Range) is installed on major roads and intersections in Guro-gu to enhance citizen safety and convenience. CCTV smart poles will be installed in alleys such as Guro 2-dong and Gaebong 1-dong to provide safe alley services.
○ In Dongjak-gu Sangdo and Sadang-ro, a smart pole that combines CCTV, public Wi-Fi, and S-DoT and a smart crosswalk will be built to improve the aesthetics of the city and establish a safe distance to prevent traffic accidents.
□ The smart pole function enhancement pilot project is a project to create a more advanced model equipped with drones and electric vehicle charging functions, which were not previously available. For example, a drone station can be mounted on the top of the smart pole to allow the drone to stay and charge. It can also be used for disaster monitoring and lifesaving by sending data to the control center. Parking and stopping monitoring functions will also be added.
□ In addition, the city plans to expand the smart pole infrastructure by first reviewing the integrated construction of various road facilities such as streetlights and traffic lights that are newly installed or replaced every year as a'smart pole'. At this time, the 10 standard models prepared this time are applied. It will spread to the city-affiliated investment and donation organizations and autonomous districts to induce the systematic establishment of smart poles throughout Seoul.
○ Currently, there are about 24 pillar-type infrastructures (street lamp posts, traffic lamp posts, CCTV holders, security lamp posts) in Seoul, and 3,500 to 3,700 units are being replaced every year with the advent of the endurance training period (replacement cost of 20 billion won as of '396). input)
○ The city will make a new amendment at the end of this year by reflecting the results of this year's smart pole enhancement pilot project and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport public offering project in the smart pole construction operation guidelines, and further enhance the smart pole standard model. Is the plan.
□ On the other hand, 10 standard models were derived by considering the types of currently installed post-type infrastructure (traffic lights, street lights, CCTV, security, etc.) and the number of possible combinations. For example, a type that combines smart functions with security lights in parks or alleys, and a type that combines smart functions with traffic lights + street lights + CCTVs in driveways can be installed.
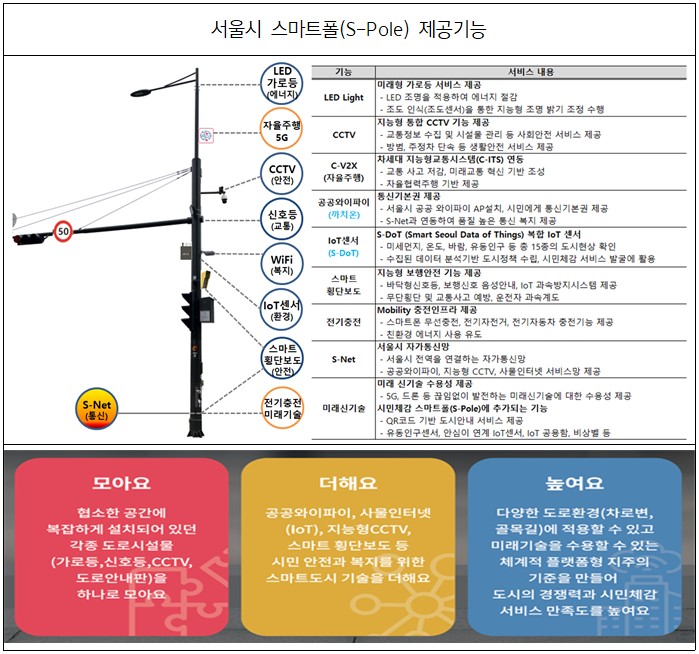
□ In the construction and operation guidelines, the standards for effectively integrating road facilities and systematically expanding and installing them throughout the city are specified to improve urban aesthetics and pedestrian convenience, and provide flexible smart functional facility plans.
○ Conduct a preliminary on-site survey from the planning stage of the smart pole installation to induce the construction of a single smart pole in which the functions of each facility are integrated if there are road facilities that can be integrated.
○ The facility structure safety review was conducted for each smart pole standard model (traffic light, street light, CCTV, security light, smart pole), and the facility standards for the safe construction of smart poles and the acceptance criteria for smart devices were specified.
○ The acceptance criteria for smart devices are used as criteria for adding new or easily replacing smart functions according to changes in construction site conditions, and acceptance criteria for new future technologies that are constantly emerging.
○ In the guidelines, the next generation intelligent transportation system (C-ITS) in Seoul and a smart pole model combined with a 5G repeater were also included, laying the groundwork for linking autonomous driving and mobile communication functions in the future.

※ Area of Youth Street, 10 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seongdong-gu, Seoul
□ The city has the effect of installing smart poles ▴Improving the aesthetics of the city through the integration of various facilities ▴Reducing replacement costs through the use of road facilities that have reached the time of replacement.
▴ Expected to secure facility safety.
□ Lee Won-mok, Seoul's Smart City Policy Officer, said, “Road facilities such as street lights and traffic lights are excellent urban infrastructure facilities installed throughout the city, but there has been a regret that it has been operated only for its own functions. 26 Smart Pole, a smart urban infrastructure that performs not only its natural functions but also various smart city functions, have been built in Seoul Plaza and Cheonggye Stream. It is expected to improve the safety, welfare, and convenience of citizens while improving the urban aesthetics. Furthermore, by adding drones and electric vehicle charging functions to the smart pole, we will develop into a smart city of Seoul.”



