– 8 University Campus Challenge·4 Cities Town Challenge Project Selection –
□ Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport explores and demonstrates smart services suitable for 2021 universities and small and medium-sized cities in the field of campus challenges for universities, among the 8 ``Smart Challenge'' project to innovatively solve urban problems. Four cities were finally selected in the field of Town Challenge.
<Selection result>
① Campus Challenge (8 universities)
-Hanshin University, Anyang University, Yonsei University, Korea National University of Transportation, Keimyung University, Sungshin Women's University, Dong-A University, Kongju University
② Town Challenge (4 cities)
-Gimcheon-si, Gyeongbuk, Gwacheon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Yangyang-gun, Gangwon-do, Osan-si, Gyeonggi-do
□ The Smart Challenge project develops smart solutions (solutions) and smart services that innovatively solve various urban problems such as transportation, safety, environment, welfare, etc. by incorporating new 4th industrial technologies (artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, big data, etc.) It is a project led by local and private sectors to demonstrate.
ㅇ (Campus Challenge) This is a smart solution demonstration project that connects to commercialization such as starting a sprout company, experimenting with innovative ideas on campus, nearby shopping centers, and downtown by participating in the participation of companies and local governments. Promote with support.
ㅇ (Town Challenge) This is a project that receives proposals for regional-specific smart solutions, such as transportation and environment, led by residents and regions through the operation of Citizen Participation Living Lab, and 30 billion won (50% of local expenses) is invested by city.
➊ (Use of University Ideas) Campus Challenge
□ For the first Campus Challenge contest held this year, 81 universities nationwide applied, and received a high 10:1 interest. Among them, artificial intelligence (AI) and data-based urban integrated control service, innovation in mobility such as personal means of transport (PM), fire safety management incorporating new technologies, and digital information gap resolution, etc. Eight universities' smart solution demonstration projects that can bring vitality to life were selected as follows.
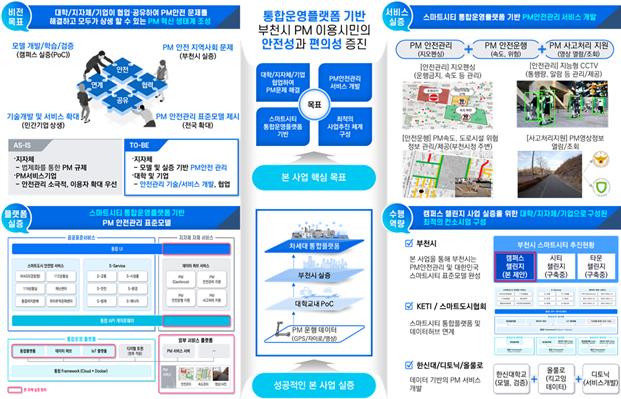
① (Hanshin University) Develop a next-generation smart city integrated operation platform model that can collect, store, analyze, and share city data from the video-centered city control network such as CCTV, which is currently in operation, and utilize this to develop personal mobility (Personal Mobility) in Bucheon City. Mobility) Demonstrate safety management services.
* A business that collects and analyzes PM operation data (videos, location information, etc.) through the integrated platform to manage speed/zone management, traffic volume analysis, abnormal situation notification and road hazard information
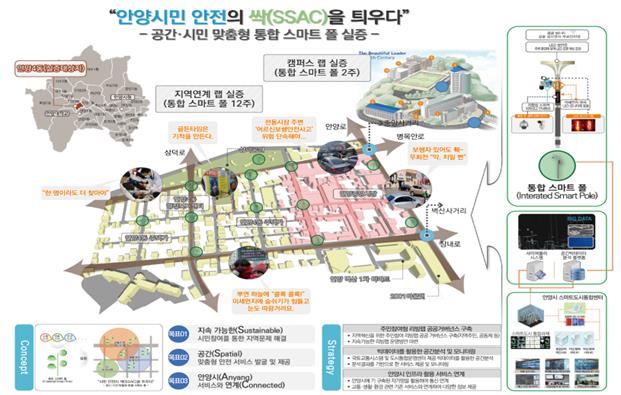
② (Anyang University) By analyzing issues using spatial big data and installing multipurpose smart poles* in the best place through residents' living labs, and linking them with Anyang City Urban Integration Center, monitoring signals, stop lines, parking and stopping violation vehicles and missing persons, etc. The intelligent CCTV city control system that performs the experiment is tested.
* (Smart poll function) Public Wi-Fi, LED security light, danger warning announcement speaker, fine dust measurement, pedestrian approach detection, automatic lighting in child protection zone, CCTV search, etc.
③ (Yonsei University) In order to solve the problem of the downturn in the commercial area of Shinchon Station, a demonstration project was proposed to increase the utility of personal mobility (PM), which can increase mobility and accessibility. It demonstrates solutions for activating commercial areas linked to PMs, such as separation of traffic lines between PMs and pedestrians, and mileage payments for demand-responsive parking induction, led by students and local communities.
* Providing safety information such as speed limit through smart helmets, providing partnership services when visiting demand-responsive PM parking lots and nearby stores (mileage payment, PM use and product integrated payment, etc.)
④ (Korea National University of Transportation) To shorten the travel time of the campus, a multi-purpose personal mobility system equipped with various functions such as leisure, logistics, and transportation, and a multi-purpose mobility station (charging, repair, etc.) was established to establish a linkage system between the autonomous driving shuttle and personal mobility. It is a business that demonstrates smart total mobility through logistics storage, cultural space, etc.)
* Self-driving shuttle (2 units) and multi-purpose personal transportation, three-wheeled bicycle for transporting small packages
⑤ (Keimyung University) In order to solve the problem of long commute and commuting time due to lack of connection of public transportation such as subway between Seongseo area and Wolbae area in Daegu, integrated transportation service (Mobility on Demand) MaaS) is planning to carry out a demonstration project.
* Real-time bus reservation using mobile app, location confirmation and arrival information of reserved vehicle, mobile payment, issuance of boarding pass, etc.
⑥ (Sungshin Women's University) The traditional market in Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, is highly concerned about electric fire accidents due to aging facilities, so it monitors electrical safety information (leakage current, load current, etc.) from the Internet of Things (IoT), and monitors big data artificial intelligence (AI). ) A project was proposed to predict electric fire risk through analysis or to demonstrate an electric safety smart control platform that supports rational decision-making.
* Detect and notify changes in electricity data, emergency dispatch service in case of abnormality, and detection of elderly people living alone through analysis of power usage patterns, etc.
⑦ (Dong-A University) In order to solve the growing and complex fire problem in old buildings in the city, 5G-based intelligent communication network and fire sensor are installed for aging public buildings (Saha Ward Office), and smart Demonstrate fire safety management services.
* Provides fire simulation learning and digital twin-based preliminary analysis and prediction/response services with real data from multiple cognitive sensors (cameras, detection sensors, etc.)
⑧ (Gongju University) To solve the problem of digital information gap caused by population decline and aging in local small towns, we use public idle facilities to provide smart service bases (digital shelters), and provide education and training that local residents want through Living Lab. The university plans to demonstrate a business that provides customized healthcare services and digital information.
* Creating a community-friendly digital shelter that provides comprehensive services such as poor digital content in small cities, a pleasant environment in the heat and cold, real estate and administrative information, etc.
➋ (Small and medium-sized city-specific solution demonstration) Town Challenge
□ Gimcheon City, which builds road hazard detection solutions to prevent traffic accidents such as road icing and animal track accidents (road kills) as a new project in the '21 Town Challenge, and Gwacheon City, Osancheon City, which seeks to solve the illegal parking problem by inducing the voluntary participation of citizens. Osan City, which protects the ecological environment and shares it with citizens, and Yangyang County, which introduces smart water control, was selected to preserve the environment and improve water quality in Namdaecheon.
① (Gimcheon) We plan to demonstrate a road hazard detection solution* that analyzes vehicle driving sounds to understand real-time road conditions and manage road hazard information. In addition, it plans to introduce road kill prevention solutions to prevent animals from entering the road and to induce drivers to slow down to prevent accidents.
* Display road signs and respond to risk factors by discriminating types of road hazards such as black ice and snow.
② (Gwacheon) As the number of illegal parking continues to increase due to the lack of parking space in the city center, a smart illegal parking integrated management solution that raises citizen awareness was proposed. It plans to smarten parking enforcement services such as mobile parking enforcement CCTV, smart fire hydrant, and bus-mounted parking enforcement monitoring, and induce voluntary moving parking of illegally parked vehicles through a parking enforcement notification system and a media board providing parking information.
③ (Yangyang) In order to preserve the environment and improve water quality of Namdaecheon, the largest salmon return river in Korea, a smart IoT irrigation system and a rainwater storage bank are introduced to automatically manage the vegetation in the river during the dry season, and to stably control the water level through automatic water gate control. It plans to build a water control solution. In addition, through the integrated hydrophilic platform, the water quality and water level data of the river will be monitored to provide information related to the river, such as the risk of flooding.
④ (Osan) We plan to protect Osancheon, which has been restored as an ecological river, and provide a smart river management service that is friendly to nature. In particular, CCTV and environmental AI patrol robots are deployed to monitor river ecology. In addition, it is expected to contribute to environmental preservation as well as vitalization of the local economy by establishing a citizen-participating eco-point system that accumulates mileage in local currency when recycling and using shared bicycles.
□ The presentation data of the selected business area can be checked through the national smart city integrated portal (www.smartcity.go.kr).
ㅇ In the future, we will focus on management so that it can be implemented as a unique solution of each region and university through expert consulting and key performance goal (KPI) specification process for each business region, and the performance cases of excellent universities and local governments are shared with other universities and local governments. · We plan to actively support so that it can spread.
* ① Project proposal (book) → ② Expert consulting → ③ Establishment of performance goals (KPI) → ④ Project promotion (Citizen Living Lab + project progress)
□Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport Urban Policy Officer Im-Rak Choi said, “The project selected this time is a typical bottom-up model in which the region and the university themselves consider solutions to solve their local urban problems. We will actively support it to become a successful model of a smart city in the living area.”
<Hanshin University>
<Anyang University>