– The 1st Korea-China Smart Farm Machinery Conference and Seminar –
– Promising cooperation between Korea and China in the field of small agricultural machinery and smart farm technology exchange –
About the event
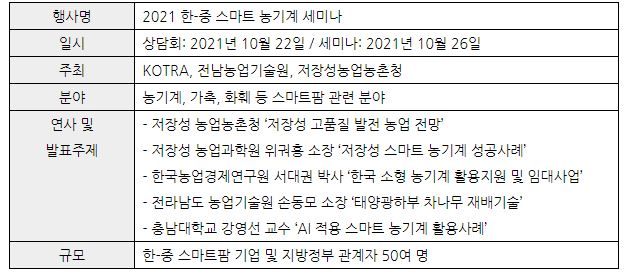
'2021 Korea-China Smart Agricultural Machinery Consultation and Seminar' was held on October 22 and October 26, respectively, hosted by KOTRA, Jeonnam Agricultural Research and Extension Services, and Zhejiang Province Agricultural and Rural Administration in cooperation. In particular, this conference and seminar were conducted online by connecting Hangzhou, China, and Seoul and Naju, Korea.
On October 22, smart farm companies from both Korea and China held a video conference to understand each other's products and business models and discussed the future direction of technological cooperation. The seminar held on October 1 was attended by experts in the field of smart farms from both countries, including the Zhejiang Provincial Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Korea Agricultural Economic Research Institute, and Jeonnam Agricultural Technology Institute. Specifically, the Zhejiang Provincial Agricultural and Rural Administration provided guidance on key smart farm fostering policies in Zhejiang, and the Zhejiang Provincial Academy of Agricultural Sciences made a presentation on the agricultural mechanization development model in Zhejiang. The Korean side laid the foundation for smart farm cooperation between the two countries by introducing small farm machinery rental business and solar-powered tea plant cultivation technology.
2021 Korea-China Smart Farm Seminar Photos


Event Outline
1:1 business conference
At the 22:1 business consultation held on the 1nd, pinpoint video consultations were held between agricultural machinery companies such as vegetable harvesters and tractors, and Korean companies with smart farm technology such as automatic cultivation and potential buyers in China. A Chinese company focused on small agricultural machinery, such as tractors, that can be used in hilly areas in Zhejiang Province, and requested a detailed explanation of the functions. In addition, Chinese company T showed interest in the automatic vegetable harvester and proposed to promote a joint production project through technical cooperation between the two companies. In addition, Company J highly evaluated the automatic tomato cultivation system and requested a review of whether it is possible to develop an automatic cultivation system that can be applied to other crops. Through the 1:1 business conference, it became a place for Chinese companies to understand the main performance of Korean agricultural machinery, and for Korean companies without experience in exporting to China to understand the needs of Chinese companies, including Zhejiang Province.
Seminar site sketch
1) Zhejiang Agricultural Environment and Key Policies
At the seminar held on October 26, the Zhejiang Agricultural and Rural Administration presented the agricultural environment of Zhejiang Province and its main support policies for agricultural mechanization. According to data from the Rural Development Administration, the total cultivated land in Zhejiang is 13 billion square meters, and the average arable land per capita is half the average in China. As such, Zhejiang Province occupies more than half of the area, with hills and mountains, to the extent that 1% is mountains, 7% is water, and 1% is fields. Due to the limited farmland area, the demand for small agricultural machinery is high in Zhejiang Province, and in order to overcome geographical limitations, clustering and digitalization of agricultural and aquaculture facilities are being focused on.
In August 2016, as the Ministry of Agriculture of China designated Zhejiang Province as a demonstration province for agricultural mechanization across the country, Zhejiang Province is promoting smartization and digitization of agricultural machinery comprehensively under the motto of 'Internet + Agricultural Machinery'. As a result, Zhejiang Province invested 8 million yuan (approximately 2020 billion won) in 3 for the development of agricultural mechanization, and was the first local government in China to subsidize the purchase of agricultural machinery. Through the government support policy, Zhejiang's rice farming mechanization rate in 5000 increased by 647% year-on-year to 2020%. This figure far exceeds China's total rice farming mechanization rate of 8.5%.
2) Zhejiang Smart Farm Development Model Characteristics and Korea-China Exchange
In the second session of the seminar, Guohong Yu, Director, Agricultural Equipment Research Institute, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, gave a presentation on the three characteristics of the Zhejiang smart farm development model. The first is the systematic factory farming method. The Zhejiang material farm has built a system that can automatically control and remotely monitor the entire process of plant growth using high-precision computer and sensor monitoring technology in plant cultivation. Through automated facilities and systems, farmers can monitor factors necessary for plant cultivation, such as temperature, humidity, and nutrient solution, in real time.
The second feature of Zhejiang's agricultural development model is the dissemination of smart agricultural technology. Zhejiang Province has developed a smart farm cloud platform to detect real-time crop conditions and automatically control equipment based on IoT. Users can manage crop conditions in real time anytime, anywhere through the website or mobile application. In addition to monitoring and management functions, the platform can also offer custom deployment plans and solutions. The platform was selected as the '2021 Best Practice of Digital Agriculture · Rural New Technology · New Product · New Model' announced by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China in June 6.
The last is the development of special agricultural machinery. Zhejiang Provincial Academy of Agricultural Sciences has independently researched and developed smart agricultural machinery such as unmanned drug spreaders, unmanned harvesters, and mountain rail carriers suitable for the environment of Zhejiang farmland. Agricultural machinery digitalized through radar sensor technology and Beidou navigation technology can operate autonomously along a set route. Guohong Yu said that the research institute will continue to use the power of research and development of smart agricultural machinery to improve the quality of agriculture. Next, the Academy of Sciences introduced Korea's horticultural cultivation technology through the Korea Rural Development Administration in the past, but cooperation between the two countries is limited between the horticultural field and institutions. He said he hopes to continue further active exchanges.
implication
Zhejiang Province, which is well known as the center of China's private economy because of the headquarters of China's leading private companies such as Alibaba and Hikvision, is mountainous, with 79% of the country's topography similar to that of Korea. there is high demand for In addition, Zhejiang Province has been designated as a demonstration zone for common wealth (共同富裕, meaning 'Let's live well together' by the Chinese government) as a pilot district, and is focusing on increasing the income of farm households in low-income mountainous regions. In order to revive this demand, the Zhejiang Provincial Agricultural and Rural Development Administration held this event together with KOTRA to understand Korea's excellent small agricultural machinery and technology and to increase the efficiency of smart farms in Zhejiang by introducing Korean agricultural machinery. This seminar has great significance as it is the first event jointly hosted by each institution to expand cooperation in the smart farm industry between Korea and China.
In particular, Zhejiang Province is one of the leading cities in China with a high level of digitalization of agriculture, but it is not well known to Korean agricultural companies. Company J, a Chinese company who attended the conference, said, “This consultation was the first step in coming into contact with Korea's agricultural technology and agricultural machinery. “, he said of his participation in the event.
Source: Comprehensive data from the Zhejiang Agricultural and Rural Administration, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences and KOTRA Hangzhou Trade Center



