– Jordanian government pushes ahead with digital transformation plan –
– Korean companies can consider participating in project bidding, private investment, partnership, etc. –
Recent trends in Jordan's ICT sector
Jordan is considered as a region with relatively developed ICT industry in the Middle East/Africa region. According to data from the Jordan Investment Commission (JIC), the ICT sector directly or indirectly generates about USD 12 billion, or 54% of Jordan’s total GDP, and more than 600 medium and large enterprises and a total of more than 8 jobs are being operated. .
According to a report by Jordan News Agency, Jordan's net ICT sector sales in 2019 were about $6.4 million, with overseas exports of $1.77 billion and domestic sales of about $4.87 billion. At this time, 85% of ICT sector exports were concentrated in five countries: UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, the United States, and the United Kingdom. In addition, Jordan is continuously implementing regulations and guidelines in the domestic wired and wireless communication field through the Telecommunications Regulatory Commission, which is the first government agency specializing in the communication sector operating in the Middle East/Africa region. About 5~5 ICT engineering college graduates are produced every year, and the Jordanian government subsidy program for these graduates is operated separately, promoting cooperation between the government, the private sector, and academia.
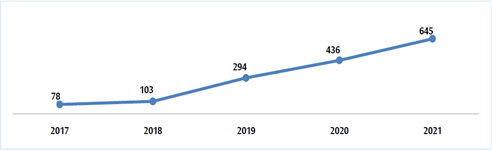
The Jordanian government has been operating an open government data platform (https://data.jordan.gov.jo) since 2017 to accelerate the integration of e-government and digital transformation. Furthermore, the Jordanian government has detailed guidelines for the operation of an open data platform to build an integrated and open e-government portal, and is continuing to promote the disclosure of related data.
Number of datasets published on Jordanian Open Government Data Platform
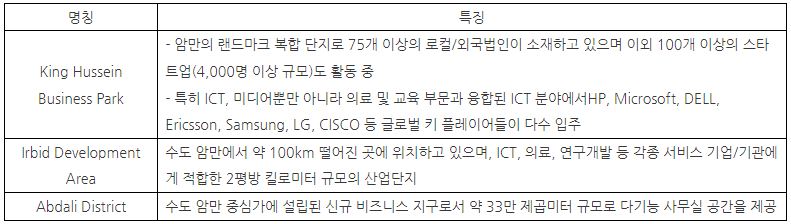
In addition, Jordan is providing various tax benefits and incentives to resident companies while operating an industrial complex for ICT companies. There are three major industrial complexes below. Major incentives for resident companies include sales tax exemption for IT services, customs duty exemption, export income tax exemption, income tax reduction on profits generated in Jordan to 3%, and products necessary for IT activities. or granting the right to use movable property, such as intellectual property rights, as collateral.
Jordan's major ICT industrial complexes
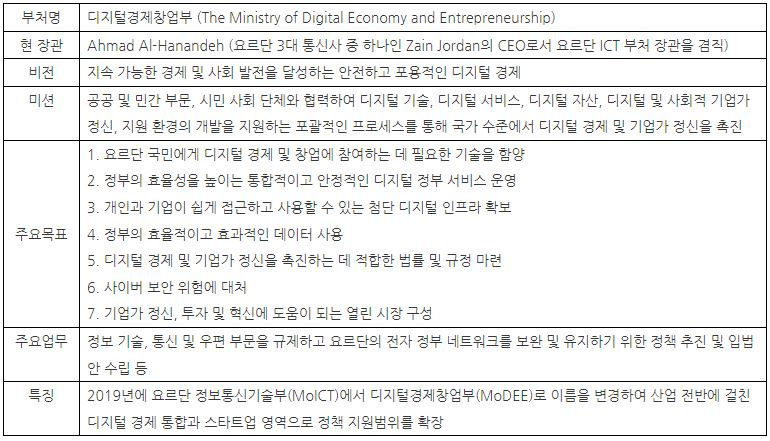
Introduction of Jordanian Digital Economy Startup Department
Interview content
Below is a visit by the KOTRA Amman Trade Office to the Jordan Digital Economy Startup Department and Mr. Digital Economy Startup Department Policy Strategy Director. This is a summary of the interviews conducted on November 3 with Tawfeeq Abu Baker and the staff of the department.
interview commemorative photo

Q1. What are the major challenges your organization is trying to solve through ICT technology?
A. Jordan is a developing country experiencing economic and resource difficulties due to its geographical location. In particular, the recent influx of millions of refugees from Syria and other countries places a burden on Jordan's water resources, energy, and logistics systems. ICT technologies can help Jordan effectively overcome the challenges and problems posed by it.
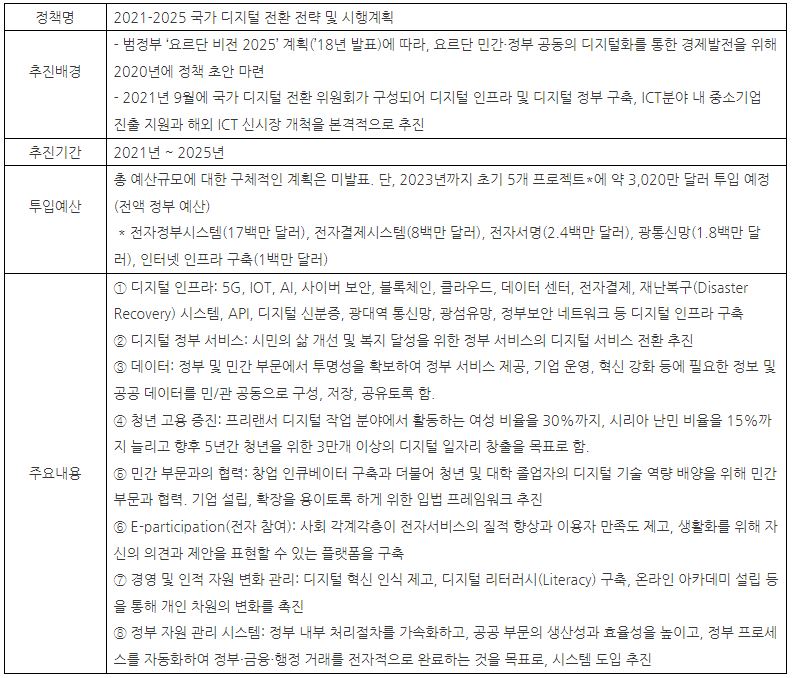
In addition, the expansion of digital infrastructure and the establishment of digital government are also urgent tasks that cannot be overlooked. The Korean government has already announced 'The national digital transformation strategy & implementation plan 2020-2021' in 2025, and the plan was approved by the Cabinet in July this year. Accordingly, our ministry is implementing various development strategies in eight sectors: digital infrastructure, digital government services, data, youth employment promotion, private sector innovation and cooperation, e-participation, change management, and government resource management.
Main contents of the national digital transformation strategy and implementation plan for 2021-2025
Q2. How can ICT technology be better applied to such multiple fields?
A. In our department, we will build a symbiotic relationship with various sectors. Through this, it is possible to maintain the ICT industry convergence strategy with industry sectors and major decision makers throughout society. Major cooperation areas include medical/health, construction/engineering, pharmaceuticals, eco-friendly technology, agriculture, tourism, education, banking and finance. Since Jordan has a weak manufacturing base, if manufacturing companies can secure competitiveness by collaborating with the national ICT sector, they will enjoy a long-term competitive advantage over other companies in the region.
Q3. What are the advantages of Jordanian public/private sector in ICT sector?
In relation to ICT, Jordan has a strong regulatory environment compared to other Middle Eastern countries. Of course, the technical skills of Jordan's ICT engineers are superior to those of neighboring countries. ProgressSoft, for example, was founded in Jordan and has an international reputation in the field of payment systems. ICT company employees can also speak English fluently. Many of Jordan's ICT company representatives have experience studying abroad in North America or Europe.
Another advantage is that Jordanian ICT companies have virtually no cultural or linguistic barriers to the Arabic-speaking neighboring markets. Therefore, advancing into the Jordanian market can mean advancing into the markets of neighboring countries. Jordan is also one of the region's most open economies to trade and foreign participation, and offers several tax-saving incentives for moving into ICT industrial parks.
Various business opportunities are also an advantage that cannot be overlooked. For instance, Jordanians have very low bank account holding rates, so FinTech solutions can provide an alternative to banking.
Q4. Then, what are the weaknesses of Jordan's public/private sector in the ICT sector or the demand for cooperation with foreign countries?
A. Jordanian ICT companies tend to focus mainly on general technology operations and sales. Jordanian companies should promote expansion into new markets through the development of innovative technologies. Only when ICT companies have a strategic and active attitude can they accumulate relevant knowledge and create competitive software.
Many Jordanian small and medium-sized ICT companies are mostly composed of engineers, developers and technical graduates with little knowledge of administrative management such as accounting, finance, and marketing. Therefore, these companies need to develop their vision and capabilities for partnership business with overseas companies, and internal management skills must be improved so that they can promote sustainable and long-term corporate growth.
Jordan also needs to improve its business environment to become internationally competitive. Our department is constantly promoting the improvement of Jordanian ICT regulations and laws, which must be internationally competitive and apply equally to all businesses. Otherwise, Jordanian businesses, management and capital could move to a more attractive environment. In addition, awareness of the importance of IPR registration is not yet high in Jordan. It is necessary to raise the awareness of ICT companies and management about technology assets.
Q5. What role do you think Korean companies can play in advancing the ICT sector in Jordan?
A. Korea is a country with a high penetration rate of smartphones and a well-developed high-speed communication network infrastructure. It is also leading the development of 5G technology and is the home of global electronics and IT companies such as Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics.
First, the know-how possessed by Korean companies can help Jordan to carry out ICT development tasks in various social fields. In addition, Korean companies can provide a variety of ICT products that streamline the lives of Jordanians.
In most cases, only local companies are given the opportunity to participate in ICT-related bidding projects conducted by the Jordanian Ministry of Digital Economy and Start-up. Therefore, Korean ICT companies can try to participate in the bidding project by securing a local agent in Jordan. For reference, our department is preparing to announce a large-scale bidding project related to the introduction of 5G communication equipment. Many telecommunication/equipment companies in Korea need to keep an eye on such bidding projects. (Details of the Jordan ICT sector bidding project can be found at https://www.modee.gov.jo/en/Modules/Tenders)
Korean companies can also seize opportunities to utilize quality labor through Jordanian companies. For example, a Korean company could outsource programming work to a small ICT company in Jordan. At this time, Jordanian SMEs can not only acquire customers and grow, but also learn the management skills of international companies. Jordan has already conducted various types of partnerships with advanced ICT countries such as the United States and China, including Korea.
Key Cases of Jordan-Overseas Business Partnership
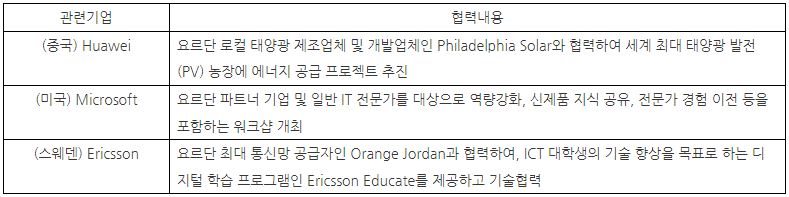
For reference, Jordan has signed the Great Arab Free Trade Agreement (GAFTA) with the Arab League of 22 countries, and has signed trade agreements for goods and services with the United States, Singapore, and the EU. It also has the advantage of easy entry into the market. At this time, Jordanian companies have sufficient capacity to carry out 'arabisation' of their software and solutions. Arabization includes not only translating internationally successful products into Arabic, but also adapting content to Arab culture. For example, with regard to audio products, the Jordanian dialect is well accepted in many countries, so if you are based in Jordan, it may be more advantageous to secure the Levant market.
implication
In 2014, the Korean government supported a project to build a Jordanian-type e-procurement system that benchmarked the Korean Nara Marketplace system. Public Procurement Service and KOICA invested about $850 million in grant aid projects, and based on this, domestic ICT companies such as KTNET supplied Jordan's electronic procurement system. This cooperative model through international aid financing is expected to play an important role in establishing a foothold for entering the Jordanian market.
In addition, the private sector can also consider entering into various ICT-related projects in the local area. Within the Jordan Project, ICT demand will be concentrated on solutions related to Jordan's current challenges, such as energy, water resources, and transportation. For example, Jordan's Transport Bureau is planning to install an eco-friendly solar bus platform in Amman's urban area where it is difficult to connect to the power grid, and the project includes the construction of a bus information system. Meanwhile, establishing a business base in Jordan and utilizing local manpower may also be considered.
Source: Jordanian Ministry of Digital Economy and Start-up, Jordan Investment Committee, various local press releases and KOTRA Amman Trade Center data



