– Global semiconductor supply shortage continues and supply prices can rise up to 200%
– Concerns about impact on cars, electronic devices, etc.
– Global semiconductor component supply and Russian market status
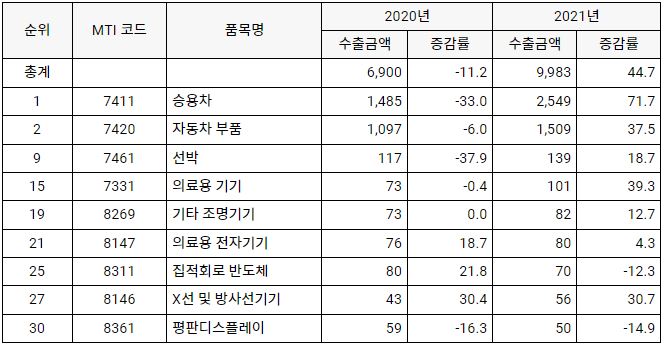
In January 2022, IC Insight, a market research firm, announced that global semiconductor parts supply deteriorated in 1, but will recover favorably in 2021. In 2022, the global semiconductor market is expected to grow 2022% year-on-year, reaching a record high of $11 billion. The integrated circuit (IC) market is expected to be worth 6806 billion dollars, and the semiconductor component (OSD) including optoelectronics, sensors, and discrete is expected to be worth 5651 billion dollars. In 1155, global IC sales grew by 2021% year-on-year and a cumulative average of 26% over the past 10 years. And the OSD division grew 7.4% year-on-year and 18% over 10 years.
<Trend of Changes in Sales Volume in the Global Semiconductor Market>
As of 2020, the size of the entire electronics market in Russia is 1 trillion rubles (exchange rate as of February 5000, 2 billion dollars), of which microelectronics products account for 23 billion dollars. Russia's microelectronic product market is known for 190% of imported products, 34% of locally developed military products, and only 82% of locally developed commercial products. As of 15, Russia's global semiconductor market share is known to be 3%.
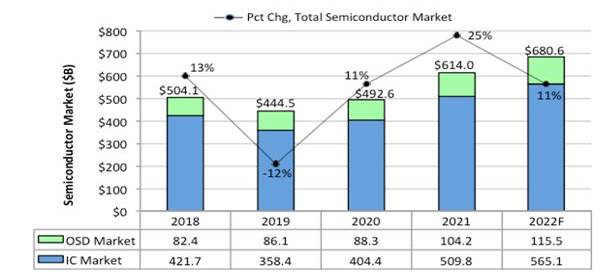
Russia is 100% dependent on imports of microchips to date. There is no local microchip production plant, and the locally produced integrated circuit (IC) is also very inferior to imported products. According to the Russian electronics sector development strategy for 2030, which is being pursued by the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation, there is a goal to increase local IC productivity by 2030 times by 2.5. By 2030, Russia's microelectronic product sales volume will be expanded to 5 trillion rubles (exchange rate as of February 2000, 2 dollars), the proportion of private manufacturers will increase to 23%, and exports will reach 658 billion dollars. Technically, it is silicon technology based on the 57.4nm (nanometer) topology standard, and the Russian government plans to invest 120 billion rubles ($5 billion) from 2021 to 2023 to develop this technology.
<Russia's '2030 Electronic Sector Development Strategy, Microelectronics Market Expansion Plan>
In January 2022, the Government of the Russian Federation announced that Lenovo, HP. Asked Acer to release laptops with Russian-made processors. The Russian government is expanding the import substitution policy to greatly increase the productivity of localized laptops, and plans to replace all laptops procured by government agencies and public institutions with local products. According to the December 1 media, the management of Lenovo Global Technology Russian corporation held a meeting with Russian government officials regarding the launch of localized laptops. Baikal Electronics is a representative manufacturer of locally manufactured processors to be installed in notebooks. The Mobile Research group plans to launch 2021 laptops based on local processors by 2023, with HP slated to ship 5 units and Lenovo and Acer the rest.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the global semiconductor market is experiencing a shortage of integrated circuits. The Russian market was also adversely affected by hardware solution price hikes and product delivery delays. In Russia, video card and set-top box manufacturers faced a production crisis due to supply cuts due to reduced demand for integrated circuits from TSMC in Taiwan. For reference, Taiwan's share of the global semiconductor market is 63%, Korea 18%, and China 6%. Deloitte experts say that another factor in the global semiconductor supply crisis is the relationship between China, the US and Taiwan. It is pointed out that the global semiconductor component market price has been greatly distorted as Huawei purchased a large amount of direct circuits just before the U.S. China's Forgein Direct Product Rule (FDPR) was applied.
<Global semiconductor parts supply by major industry (based on sales)>
Meaning of US sanctions against Russia for semiconductor technology and components
According to SBS Consulting (market analysis), the industry that is most affected by the global semiconductor supply shortage from 2020 is the automobile industry. On average, 1 to 200 semiconductor modules are installed per new car, and global automobile production fell 3000% in 2021 compared to 2018. This decline in automobile productivity also occurred in Russia in 15. Local productivity of Fiat, Chrysler, GM, Audi, and Volvo, which entered the Russian automobile manufacturing industry, fell sharply, and AvotVAZ, a local assembly company specializing in foreign brand automobiles, also experienced the same situation. The Russian government made ERA-GLONASS (emergency rescue request modem, developed in Russia) mandatory for vehicles manufactured and distributed locally to localize semiconductor parts, but the compulsory requirement was temporarily lifted until the first half of 2021 due to the global semiconductor supply shortage.
In addition to the global semiconductor supply shortage, if the U.S. applies the Foreign Direct Product Regulation (FDPR) to semiconductors supplied to Russia, the production of Elbrus CPUs, which Russia has ambitiously developed in the meantime (TSMC is also in production), will suffer a great blow. 5~7nm) CPU and GPU-equipped products cannot be supplied to the Russian market. And the opening of 5G communication is expected to be extended indefinitely. For reference, the CPU and GPU technology developed by Russia itself is 14nm or higher.
If FDPR is applied to the supply of semiconductor technology and parts to the US, all semiconductor-equipped products supplied (exported) to Russia are subject to the strict De Minimis Rule of the US Department of Commerce (US Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Safety). A secondary boycott may be applied if the rules are blocked or the rules are violated.
On the other hand, there is a scenario that Russia's own technology development will become a reality due to US sanctions and that the foundry business can be pursued with these technologies, but it is difficult to say how many years it will take with the current Russian technology. On the other hand, even if export according to the US minimum content calculation rule is possible, it is necessary to keep in mind the possibility that the export unit price may increase by 150-250% due to complicated procedures and costs.
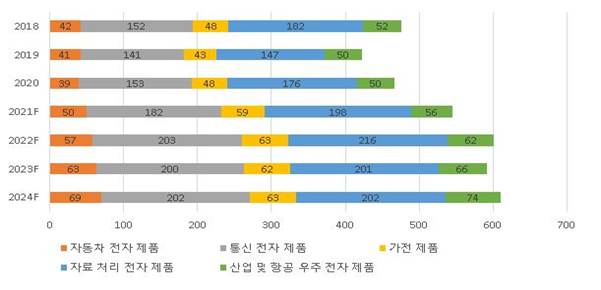
<Items affected by semiconductor sanctions among items exported to Russia>
(Unit: US$ million, %)