Indonesian smart city market expected to grow at an average annual rate of 2028% by 14.9
'Smart City', which is defined in various ways by country and institution, generally integrates new technologies such as ICT and big data into cities to ① improve the quality of life of citizens, ② improve the efficiency of urban management, and ③ sustain the city. model that makes it possible. (Source: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport, 2019-2023 Smart City Comprehensive Plan)
The smart city market can be divided into 'Green Field', a method through the construction of new cities, and 'Brown Field', a method that provides problem-solving solutions to existing cities. In the case of Indonesia, the New Capital City relocation project (Nusantara_New Capital City of Indonesia) is a greenfield type, and the 100 smart city project (Gerakan 100 Smart City) is a representative example of a brownfield type.
The smart city market continues to grow in that it is an effective means to respond to climate change as well as to solve the rapidly increasing urbanization problem. In particular, ASEAN countries including Indonesia are actively promoting smart city development to discover new growth engines. On the other hand, the importance of the smart city market is expanding in terms of expanding overseas project orders for Korean companies. This is because the smart city market has the characteristics of ① high value-added projects, ② areas of competitive advantage, and ③ possibility of overcoming local content constraints.
The KOTRA Jakarta Trade Center would like to introduce the characteristics of the Indonesian smart city market that Korean companies should pay attention to by analyzing the trends of the Indonesian smart city market.
Growing Indonesian smart city market
According to a report by 'Grand View Research', a global research and research company in December 2022, the global smart city market size is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 2023% from 2030 to 25.8, reaching $2030 trillion in 6. Meanwhile, the research firm estimated the size of the Indonesian smart city market at $9652 billion in 2020, and predicted an average annual growth rate of 98% from 2021 to 2028. It is noteworthy that the growth of the Indonesian smart city market is a means of solving urbanization and climate change problems and a means of securing new growth engines.
① A means to solve urbanization problems
The 2018 UN's 'World Urbanization Prospects Report' predicts that the global urban population will reach 2050% by 68, and analyzes that 30% of the 25 billion people who will newly settle in cities over the next 90 years will be concentrated in Asia and Africa. did. Meanwhile, in the case of Indonesia, the Ministry of National Development and Planning (BAPPENAS) and the Ministry of Environment and Forestry (Kementerian LHK) have predicted that 2045% and 67% of Indonesia's total population will live in cities in 82.4, respectively.
According to a survey by the Korea Land and Housing Corporation (New Capital Infrastructure TF Team) in 2022, 6.7% of the population and 56.6% of GDP are concentrated in Java, which accounts for 58.5% of Indonesia's land area. 0.3% of the population is concentrated in the % region. This overcrowding phenomenon in cities causes social and economic problems such as lack of housing and drinking water, deterioration of environment and sanitation, and traffic congestion in the city. This leads to increased demand for urban infrastructure, such as urban sewage treatment and transportation system reorganization. Indonesia is exploring the use of smart city technology as a means of solving the problem. In particular, in the case of relocation to a new city, efforts are being made to overcome the limitations of the city's physical infrastructure by considering smart city design from the construction stage.
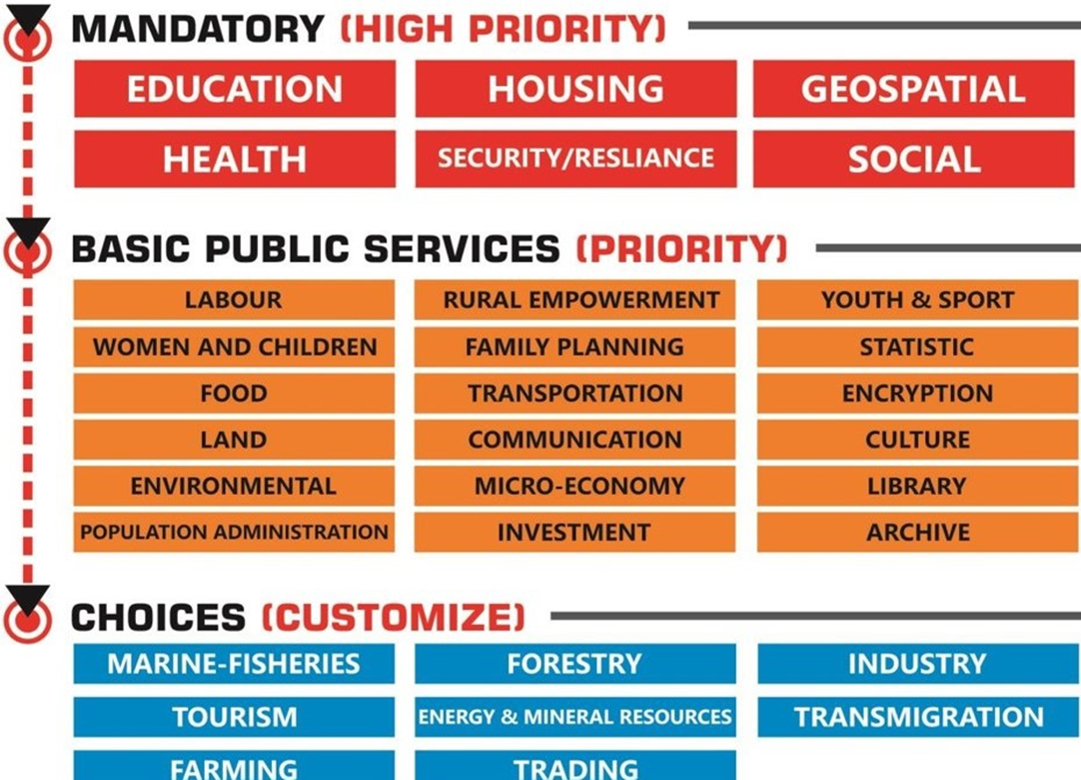
Meanwhile, in order to improve the quality of life of citizens concentrated in cities and improve the efficiency of urban management, the Indonesian government compulsory compliance with Indonesian national standards (city) (Presidential Decree No. 2022, 59) and establishment of an e-government system (December 2022). Presidential Decree No. 132, 2022) issued regulations. As a result, the growth of the smart city market is expected to be prominent in six fields, including education, housing, and security, which are mandatory smart city services prescribed by the Indonesian government in 2014, and in the ICT field, such as data integration platforms.
<Indonesian smart city priorities by sector>
[Source: Ministry of Interior of Indonesia]
② Means to solve the climate change problem
The UN's 'Global Sustainable Development Report' in 2019 analyzed that energy consumption and carbon emissions are concentrated in cities, which account for only 2% of the world's area, and in particular, 75% of carbon emissions occur in cities. Professor Kim Do-yeon of Sungkyunkwan University, who served as the chairman of the National Smart City Committee, said in an interview with The AI in 2021 that “cities are acting as a cause of climate change, and cities have the solution, too.” There is,” he said.
As smart cities emerge as an effective means of responding to climate change, the movement to solve climate change problems using smart cities in each country is accelerating. Korea's 'Eco Smart City' and Japan's 'Super City' are representative examples. Indonesia is actively using smart cities as a means of solving climate change problems by establishing major development principles such as using 75% or more green area and 100% renewable energy in relation to the relocation of the new capital. In addition, with the goal of reducing national carbon emissions by 2030% by 29, various projects such as the construction of waste-to-energy conversion facilities and the construction of renewable energy power plants are being promoted together.
<Main Principles and KPIs for New Capital Development in Indonesia>
Note: Key principles and KPIs related to addressing climate change issues
[Source: Indonesia National Development Planning Department, Korea Land and Housing Corporation (New Capital Infrastructure TF Team)]
③ Means of securing new growth engines
ASEAN countries including Indonesia are actively promoting smart city development to discover new growth engines.
In an interview with CNBC in August 2022, Minister Bambang of Indonesia's new capital said, "The project to relocate the new capital will play an important role in achieving Indonesia's goal of entering high-income countries by 8." Indonesia is actively attracting foreign investment in related fields to utilize smart city as a new growth engine. In particular, in the case of projects related to the creation of an eco-friendly urban ecosystem in Shinsudo, the government regulation (No. 2045/100 ) was published. On the other hand, according to an interview with Indonesian project expert A, the Indonesian government has restricted foreign companies from participating in projects by the 'user charge' method, but in the case of smart city projects such as new capital relocation, 'government payment (Availability Payment)' method is also being considered.
Note: User Charge: The project company directly collects usage fees from facility users.
Availability Payment: The government pays a certain amount to the project company. Market risk is borne by the government, so it is evaluated as a favorable condition for companies.
Strategies for entering the Indonesian smart city market
According to the 'Smart City Overseas Expansion Activation Plan' announced by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport in 2019, Korea has more than 20 years of new city development experience, high-speed information communication network, and ICT infrastructure such as urban integrated operation centers that are world-class. It has secured international competitiveness in the smart city field. In order to support the smart city project, the Korean government carried out economic diplomacy through the One Team Korea Export Support Group, as well as the Smart City Overseas Cooperation Center of the Korea Trade-Investment Promotion Agency (KOTRA) and the Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement (KAIA). Through the K-CITY NETWORK, etc., we actively support the establishment of local networks for companies that have entered the market. In addition, we would like to introduce strategies for entering the Indonesian smart city market that Korean companies can utilize.
① Utilization of our company's smart city project promotion information
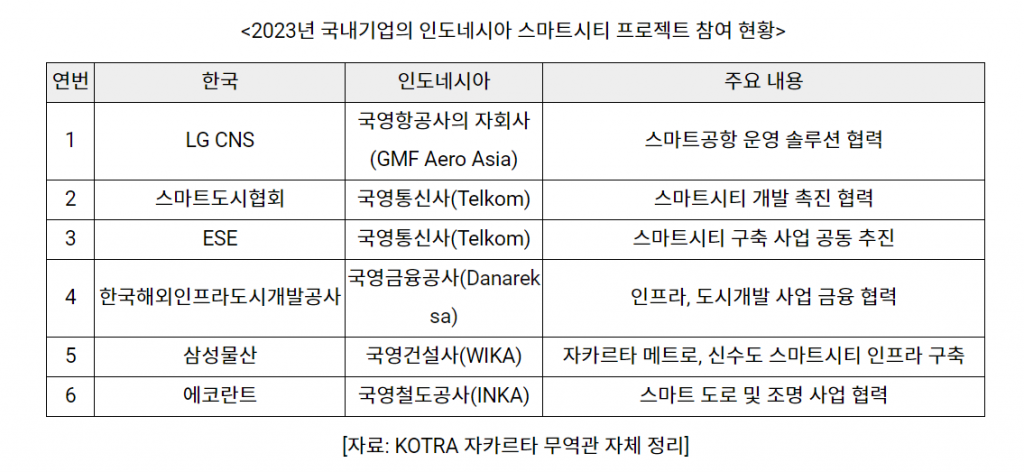
In the case of our company, despite its excellent technology, participation in the project is limited due to the lack of network with the Indonesian government agency and the private sector. Therefore, it may be necessary to take an approach in which Korean companies, government agencies, etc. utilize project information that is already being pursued to secure an advantageous position in order to win orders, such as related operations and supply of equipment and materials. In addition, through the 'Smart City Overseas Cooperation Center' of the KOTRA Jakarta Trade Center, local partners can be discovered for joint project implementation and information on promising projects can be supported.
② Participation in projects led by multilateral development banks (MDBs) such as the World Bank and Asian Development Bank
The MDB project is characterized by stable financing and fair bidding, making it suitable for small and medium-sized companies to advance into the market. Information on MDB-led projects being promoted or planned in Indonesia can be easily found through the link below.
· World Bank: https://www.worldbank.org/en/home
· Asian Development Bank: https://www.adb.org/
Meanwhile, you can check related information by attending the MDB Project Plaza held by KOTRA. In 'MDB PROJECT PLAZA 2022', KOTRA supported 206 consultation arrangements between 36 domestic companies and clients for projects worth $132 billion. (2023 project participation inquiry: KOTRA Infrastructure and Energy Industry Team)
③ Participation in private-led smart city projects
As smart city projects by Indonesian private companies are making significant progress, it is also necessary to pay attention to related markets. PT that develops and operates Kota Jababeka Cikarang, the largest industrial complex in Southeast Asia. Jababeka Tbk signed an agreement with the Hong Kong Smart City Consortium for the development of a smart city in Kota Jababeka in 2020, including a power plant, waste treatment plant, wastewater treatment plant, logistics solution center, high-speed fiber optic network, and 24-hour security. We are accelerating the realization of industrial complexes.
Sinar Mas Land, one of Indonesia's largest real estate developers, is collaborating with Abu Dhabi-based Group42 to develop BSD City into a smart city by utilizing innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing. Sinar Mas and Group24 will implement a smart city and smart campus platform, aiming to build a unified platform for services in security monitoring, building access, payment, e-commerce, advertising, education and healthcare.
implication
In order to enter the growing Indonesian smart city industry, it is most important to understand the characteristics of the Indonesian smart city market. In addition to the characteristics mentioned, it is worth noting that the Indonesian smart city market prefers investment development (PPP) projects. According to Indonesia's 2020-2024 National Medium-Term Development Plan (RPJMN), the Indonesian government has set a target of allocating around 6.2% of GDP to infrastructure spending. However, as of 2022, the actual Indonesian government's infrastructure-related budget is about 2358 trillion rupiah, which is only about 37% of the target amount. The Indonesian government is trying to raise funds by actively inducing the participation of the private sector through public-private joint ventures and investment development projects.
Indonesia tends to prefer investment development (PPP) projects when promoting smart city projects for the above reasons. In order for a Korean company, a foreign company, to participate in the Indonesian PPP project, it is necessary to closely understand the project details, registration procedures, and related laws of the PPP Book announced by the Indonesian government every year. As a follow-up to this news, the KOTRA Jakarta Trade Center will introduce interviews with Indonesia's PPP-approved organizations along with procedures and plans for Korean companies to participate in the PPP project.
On the other hand, you can use the help of the KOTRA Jakarta Trade Center's Smart City Overseas Cooperation Center* or participation in local exhibitions to identify market demand and discover potential partners. The KOTRA Jakarta Trade Center discovers information on about 40 promising projects every year and supports domestic companies of interest in finding local partners. In addition, the Smart City Expo will be held in Jakarta, Indonesia from August 2023 to September 8, 30.
Note*: Discovery of promising projects, discovery of potential partners, network establishment support, etc. (Manager Kim Hee-soo, smilewater@kotra.or.kr)
Note**: 2023 Indonesia Smart City Expo (IISMEX): 2023.8.30.~9.1., Jakarta, Indonesia, https://iismex.com/
The Indonesian presidential election scheduled for 2024 is acting as a political factor that puts pressure on the current regime to create tangible results. In addition, according to the government-led new capital relocation plan, the growth of the Indonesian smart city market is expected to continue in the future. In addition to Korea's new city development experience and world-class ICT technology, it is expected that it will be a good opportunity for Korean companies to win overseas projects if they understand and approach the characteristics of the Indonesian smart city market.
Source: Indonesia Ministry of Public Works and Housing, Indonesia New Capital Authority, Indonesia National Development Planning Department, Indonesia Ministry of Home Affairs, Indonesia Smart City Association, Korea Land and Housing Corporation New Capital Infrastructure TF Team, International Economic Policy Institute, Grand View Research, Asosisi Prakarsa Indonesia Cerdas, UN , Korea Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport, Korea Smart City Association, THE AI, etc. KOTRA Jakarta Trade Center data collection